Use the following linux command as root user to check if a port is blocked on your machine or not.
Copy the command. Replace <PORT> with actual port number e.g. 22 and run it on bash terminal.
for tcp ports :
#start port=<PORT>; (iptables -nL INPUT | head -1 | grep "DROP" > /dev/null || \ ( echo -e "\nPort $port is $(tput setaf 2)Allowed$(tput sgr0 0)\n" && false )) && ((iptables -nL INPUT | grep tcp.*:$port > /dev/null && \ echo -e "\nPort $port is $(tput setaf 2)Allowed$(tput sgr0 0)\n") || \ echo -e "\nPort $port is $(tput setaf 1)Blocked$(tput sgr0 0)\n") #end
for udp ports:
#Start port=<PORT>; (iptables -nL INPUT | head -1 | grep "DROP" > /dev/null || \ ( echo -e "\nPort $port is $(tput setaf 2)Allowed$(tput sgr0 0)\n" && false )) && ((iptables -nL INPUT | grep udp.*:$port > /dev/null && \ echo -e "\nPort $port is $(tput setaf 2)Allowed$(tput sgr0 0)\n") || \ echo -e "\nPort $port is $(tput setaf 1)Blocked$(tput sgr0 0)\n") #end
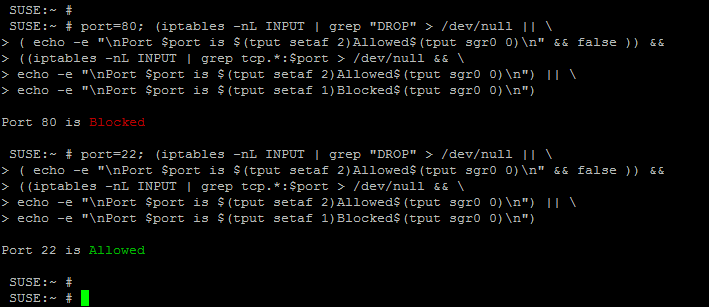
Following image shows examples of checking if HTTP ports 80(http) and 22(ssh) are enabled on the server or not.
NOTE : This command does not consider ports defined in ranges.